July 2023 is set to be the hottest month on record
Bonn and Geneva (Copernicus and WMO) - According to ERA5 data from the EU-funded Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S), the first three weeks of July have been the warmest three-week period on record and the month is on track to be the hottest July and the hottest month on record. These temperatures have been related to heatwaves in large parts of North America, Asia and Europe, which along with wildfires in countries including Canada and Greece, have had major impacts on people’s health, the environment and economies.

« We don’t have to wait for the end of the month to know this. Short of a mini-Ice Age over the next days, July 2023 will shatter records across the board, » said United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres.
« According to the data released today, July has already seen the hottest three-week period ever recorded; the three hottest days on record; and the highest-ever ocean temperatures for this time of year, » Mr Guterres told journalists at UN headquarters in New York.
« For vast parts of North America, Asia, Africa and Europe – it is a cruel summer. For the entire planet, it is a disaster. And for scientists, it is unequivocal – humans are to blame. All this is entirely consistent with predictions and repeated warnings. The only surprise is the speed of the change, » said Mr Guterres.
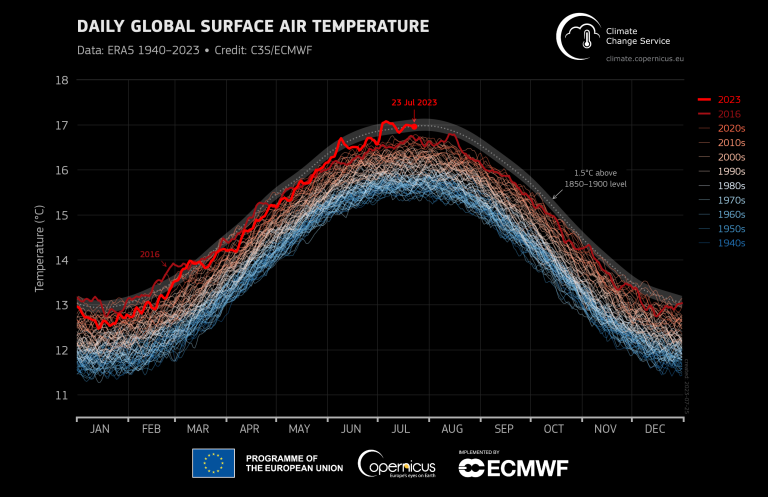
On July 6, the daily average global mean surface air temperature surpassed the record set in August 2016, making it the hottest day on record, with July 5 and July 7 shortly behind. The first three weeks of July have been the warmest three-week period on record. Global mean temperature temporarily exceeded the 1.5° Celsius threshold above preindustrial level during the first and third week of the month (within observational error). Since May, the global average sea surface temperature* has been well above previously observed values for the time of the year; contributing to the exceptionally warm July.It is extremely likely that July 2023 will be the hottest July and also the hottest month on record, following on from the hottest June on record. According to ERA5 data the previous hottest month on record was July 2019. Complete ERA5 data for July will be available and published by C3S in their upcoming monthly bulletin on August 8.
It is extremely likely that July 2023 will be the hottest July and also the hottest month on record, following on from the hottest June on record. According to ERA5 data the previous hottest July and month on record was July 2019. Complete ERA5 data for July will be available and published by C3S in their upcoming monthly bulletin on August 8.
WMO consolidates data from C3S and five other international datasets for its climate monitoring activities and its State of the Climate reports.
Carlo Buontempo, Director of the Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) at ECMWF, comments: “Record-breaking temperatures are part of the trend of drastic increases in global temperatures. Anthropogenic emissions are ultimately the main driver of these rising temperatures”. He added “July’s record is unlikely to remain isolated this year, C3S’ seasonal forecasts indicate that over land areas temperatures are likely to be well above average, exceeding the 80th percentile of climatology for the time of year”.
“The extreme weather which has affected many millions of people in July is unfortunately the harsh reality of climate change and a foretaste of the future,” said World Meteorological Organization’s Secretary-General Prof. Petteri Taalas. “The need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions is more urgent than ever before. Climate action is not a luxury but a must.”
WMO predicts that there is a 98% likelihood that at least one of the next five years will be the warmest on record and a 66% chance of temporarily exceeding 1.5°C above the 1850-1900 average for at least one of the five years.
This does not mean that we will permanently exceed the 1.5°C level specified in the Paris Agreement which refers to long-term warming over many years.

