New Coalition on health, environment and climate change is launched
The heads of the World Health Organization (WHO), UN Environment and World Meteorological Organization (WMO) have launched a new global coalition on health, environment and climate change. One of its overall goals is to reduce the annual 12.6 million deaths caused by environmental risks, and especially air pollution.
The heads of the World Health Organization (WHO), UN Environment and World Meteorological Organization (WMO) have launched a new global coalition on health, environment and climate change. One of its overall goals is to reduce the annual 12.6 million deaths caused by environmental risks, and especially air pollution.
 WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, UN Environment Executive Director Erik Solheim and WMO Secretary-General Petteri Taalas briefed delegates at the annual World Health Assembly on the priorities, opportunities and challenges in the months and years ahead.
WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, UN Environment Executive Director Erik Solheim and WMO Secretary-General Petteri Taalas briefed delegates at the annual World Health Assembly on the priorities, opportunities and challenges in the months and years ahead.
“If we want to achieve Health For All, we will need to keep health costs down and that means three things: prevention, prevention, prevention,” said Dr Tedros. “We must ensure people can breathe clean air, drink clean water, and eat nutritious food."
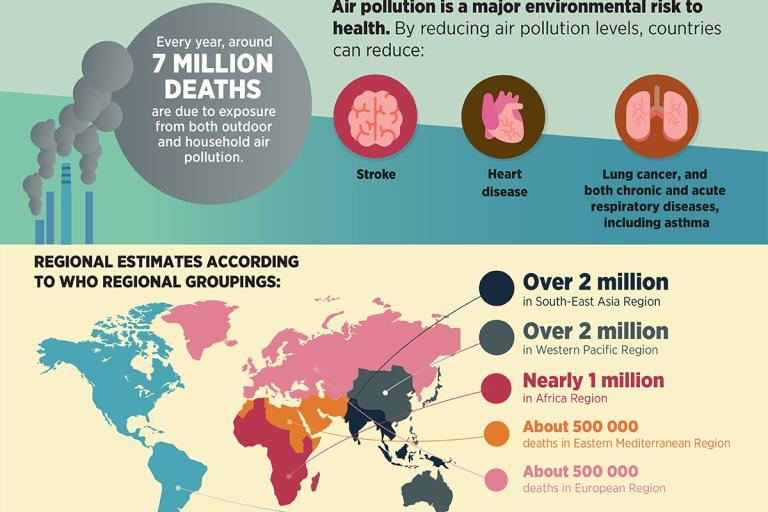
According to WHO figures, an estimated 7 million people die prematurely every year from air pollution related diseases, including strokes and heart disease, respiratory illness and cancer. Air pollution in most major cities exceeds WHO air quality standards.
Many pollutants which damage health also harm the environment and contribute to climate change. These include black carbon from diesel engines, cooking stoves and waste incineration, and ground level ozone, which are harmful but are short lived in the atmosphere. It is estimated that reductions in short-lived climate pollutant emissions from sources like traffic, cookstoves, agriculture and industry could help trim the rate of global warming by about 0.5°C by 2050.
WMO chief Taalas highlighted the need to tackle short-lived pollutants but said the top challenge was in cutting emissions of carbon dioxide, the main gas driving climate change. This remains in the atmosphere and oceans for many thousands of years.
Global average concentrations of CO2 in 2017 exceeded 400 ppm, and average temperatures were 1.1°Celsius above pre-industrial levels. Climate change is adversely affecting economies in developing countries, and the cost of natural disasters, in particular tropical cyclones, hit a new record last year, said Mr Taalas.
He urged greater urgency in implementing the Paris Agreement on climate change to keep the temperature increase to under 2°C by the end of this century.
"Realistically we are talking about 2-4°C. If we use all of the fossil fuel resources we will reach 8°C,” he said.
Mr Taalas said the world has a “30 year window of opportunity” to reduce the carbon footprint, reign in greenhouse gas emissions and to switch to clean and renewable energy in pursuit of the “win-win solution” of tackling both climate change and pollution.
The urgency of combating pollution in countries like China has given new impetus to the drive to cut greenhouse gas emissions and tackle long term climate change, said Mr Solheim.
“If we speed up on renewable energy solutions, fewer people will die from air pollution. Let’s create a pollution free environment," he said.
WMO already closely collaborates with both the WHO and UNEP, but within the new coalition called for at COP22 in Marrakesh, WMO (through national meteorological services) will strengthen action specifically targeting health protection from environment and climate change related risks.
This will be through better provision of climate services such as seasonal outlooks can improve management of climate-sensitive diseases like cholera and malaria, heat-health warnings against the growing problem of heatwaves, and multi-hazard early warning services against high-impact events like tropical cyclones.
The coalition begins with a joint focus on Air Quality outlining five areas of joint work. WMO’s observing network, its Sand and Dust Storm Warning, Advisory and Assessment System (SDS-WAS) and its Global Atmosphere Watch stations, which monitor the atmosphere, will be underpinning to the global drive to improve air quality mapping and monitoring.
The SDS-WAS can play an important role in knowing when and where dust storms may occur, to allow health partners to plan more effectively and benefit from WMO global atmospheric monitoring and forecasting capacity on acute episodes of hazardous air quality – such as dust storms.
The new global coalition on health, environment and climate change will seek to pool expertise and achieve greater coordination. One of the most immediate outcomes of the coalition will be a Global Conference on Air Pollution and Health, which will take place in Geneva 30 October to 1 November.










